Understanding Condensation Walls in Air Conditioning Systems
- Home
- Understanding Condensation Walls in Air Conditioning Systems
-
By: aadmin
- Comments Off on Understanding Condensation Walls in Air Conditioning Systems
Understanding Condensation Walls in Air Conditioning Systems
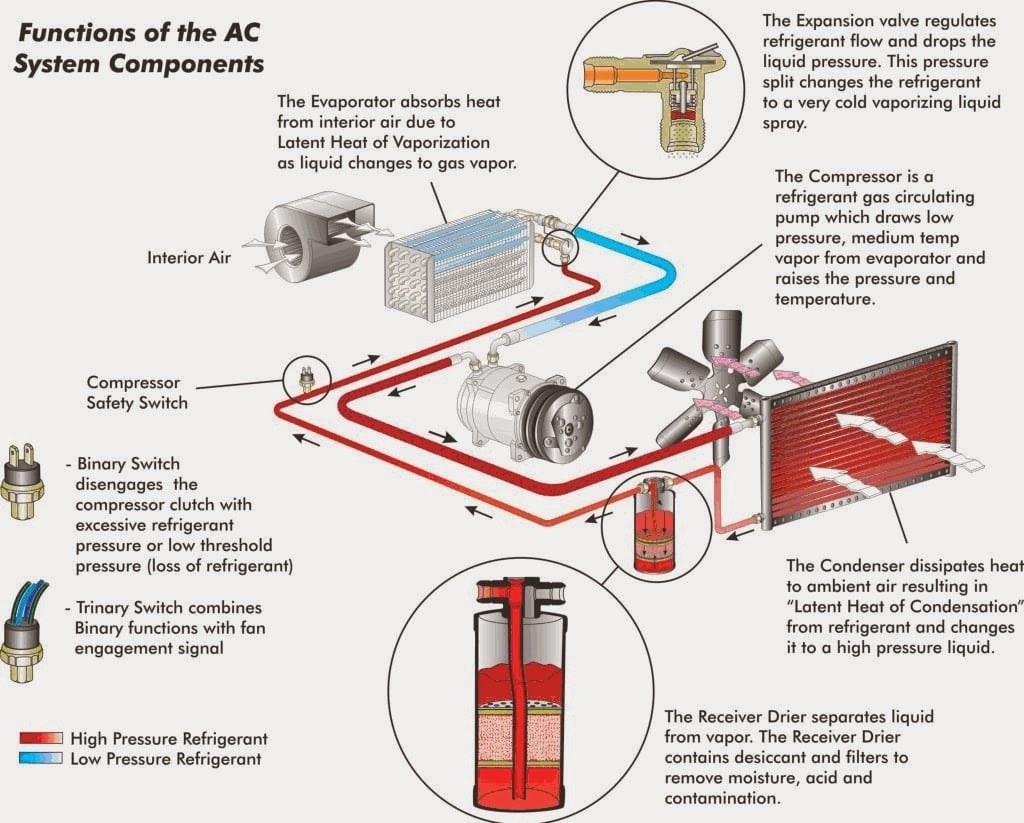
In the realm of air conditioning systems, condensation walls play a crucial role in maintaining indoor comfort and preserving the integrity of buildings. Understanding how condensation walls function, their significance, and methods to mitigate potential issues is essential for both homeowners and HVAC professionals. This article aims to delve into the concept of condensation walls, their operation, common problems, and solutions.
What is a Condensation Wall? A condensation wall, also known as a dew point wall, is a surface within an air conditioning system where moisture from the air condenses due to temperature differentials. When warm, moist air comes into contact with a surface that is cooler than its dew point temperature, water vapor in the air transforms into liquid water, leading to condensation.
Operation of Condensation Walls: Condensation walls are typically found in HVAC ductwork and around air handling units. As air passes through the system, it undergoes temperature changes. When the air reaches its dew point temperature, moisture begins to condense on surfaces, forming droplets. These surfaces can include duct walls, coils, and other components of the air conditioning system.
Significance of Condensation Walls: Condensation walls play a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality and preventing moisture-related issues within buildings. By removing excess moisture from the air, condensation walls help prevent mold and mildew growth, which can cause health problems and damage to property. Additionally, condensation walls help improve the efficiency of air conditioning systems by ensuring proper moisture removal and temperature control.
Common Problems Associated with Condensation Walls: Despite their importance, condensation walls can experience various problems that may compromise their functionality and effectiveness. Some common issues include:
Insufficient Insulation: Inadequate insulation of ductwork or air handling units can lead to temperature differentials that cause condensation to form on adjacent surfaces.
Poor Drainage: If condensate cannot properly drain away from surfaces, it may accumulate, leading to water damage and microbial growth.
Air Leakage: Air leaks in ductwork or around air handling units can introduce warm, humid air into the system, increasing the likelihood of condensation formation.
Improper System Design: Design flaws in the air conditioning system, such as incorrect sizing or placement of components, can contribute to condensation problems.
Solutions to Condensation Wall Issues: Addressing condensation wall issues requires a combination of proper design, maintenance, and remediation strategies. Some effective solutions include:
Improved Insulation: Adding insulation to ductwork and air handling units can help maintain consistent temperatures and reduce condensation formation.
Enhanced Drainage Systems: Installing or upgrading drainage systems to efficiently remove condensate from surfaces can prevent water buildup and associated problems.
Sealing Air Leaks: Identifying and sealing air leaks in ductwork and around air handling units can prevent the infiltration of warm, humid air into the system.
Regular Maintenance: Conducting routine inspections and maintenance of air conditioning systems can help identify and address condensation wall issues before they escalate.
Conclusion: Condensation walls are integral components of air conditioning systems, playing a vital role in maintaining indoor comfort and preventing moisture-related problems. Understanding the operation of condensation walls, common issues associated with them, and effective solutions is essential for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of HVAC systems. By implementing proper design, maintenance, and remediation measures, homeowners and HVAC professionals can mitigate condensation wall issues and promote a healthy indoor environment.